What is the Bitcoin Lightning Network?
Bitcoin’s Lightning Network was first proposed in 2015 by American researchers Thaddeus Dryja and Joseph Poon. The two published a whitepaper outlining their philosophy for a Bitcoin scaling solution which built on the work and ideologies of Bitcoin founder Satoshi Nakamoto.
In 2018, software developers Lightning Labs further developed the ideas of Dryja and Poon and released a beta version of the Lightning Network. Today, over 300 companies, projects and apps make up the Lightning ecosystem with it becoming more and more common for companies to accept payment via Bitcoin Lightning Network.
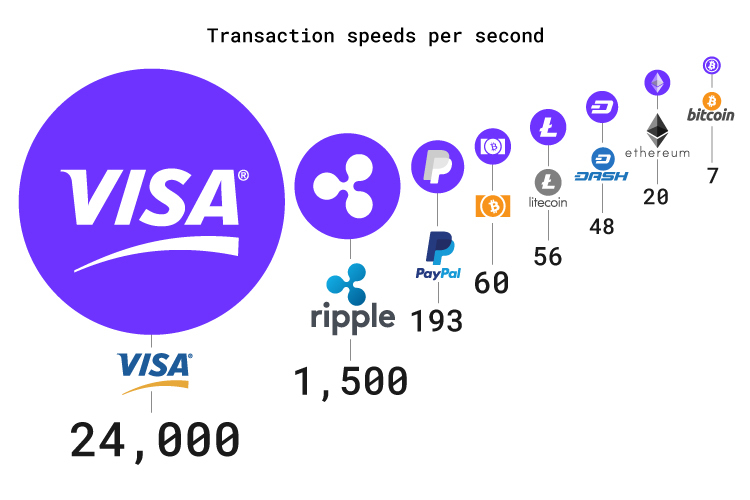
The underlying aim of Bitcoin Lightning was to create a faster, more efficient network which would allow Bitcoin to perform more transactions per second than the main network can (which has a theoretical maximum speed of just 7-10 tps and can take over an hour to confirm a transaction).
Ultimately, the Lightning Network would allow BTC to be used for everyday smaller payments, similar to traditional payment facilitators such as Visa, while not congesting the main network.
Lightning Labs began developing a layer-2 network which works through peer-to-peer connections, allowing transactions to take place off the main Bitcoin network to provide users with a faster alternative for smaller Bitcoin transactions.
Transferring BTC on the main Bitcoin blockchain involves submitting a transaction which then needs to be included in a block for it to be confirmed by validators. Only then can the amount be credited to the receiver’s account. This process means everyone who submits a transaction is competing for space on the block.
Depending on how many users are competing at any given time, the transaction costs on average $1 and takes around 20 minutes to complete. With Lightning, each small transfer is completed almost instantly and the fee is minimal due to the fact that only once the connection to the Lightning channel is closed, does the transaction get submitted to the Bitcoin blockchain.
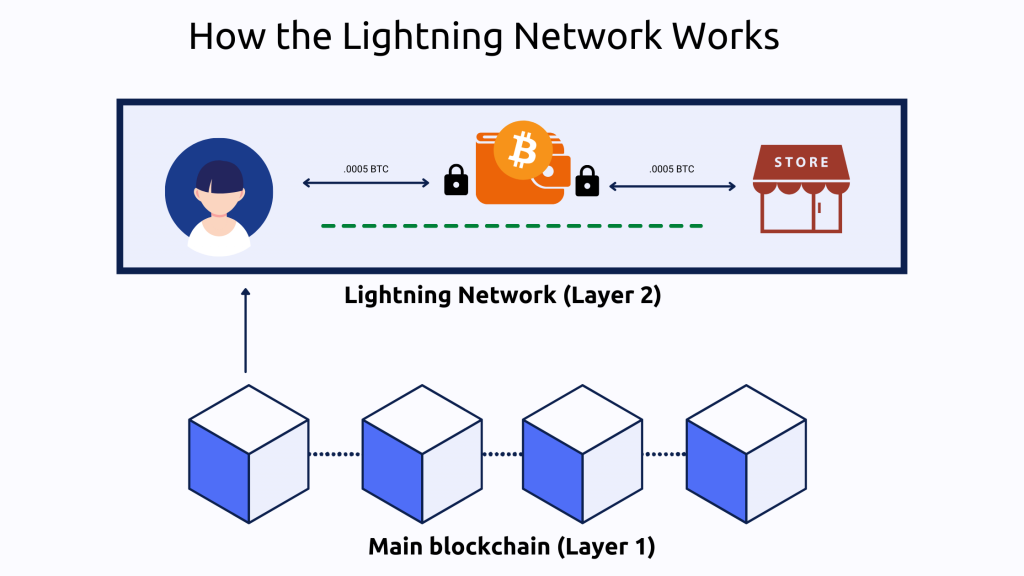
As a result, Bitcoin users can complete everyday transactions using BTC for items such as groceries, coffee or lunch without having to pay a high transaction fee for each payment or standing around for 20 minutes while their transaction is confirmed.
Essentially, the Lightning Network facilitates Satoshi’s ultimate vision: to make BTC a viable replacement for fiat.
How does the Lightning Network work?
Getting into the specifics of how Bitcoin Lightning works is a bit technical, but we’ll break it down in this section so that you know exactly what is happening for anyone sending or receiving BTC using Lightning wallets.

Firstly, the user will need a Lightning compatible wallet which can transact with other Lightning wallets.
They then need to fund the wallet with BTC so they can then establish a connection with a Lightning channel by depositing the BTC. This allows them to send and receive Bitcoin from all other users in the channel almost instantly.
Depositing Bitcoin into a channel ensures that, while a user is connected to a channel, they can send their deposited BTC to others cheaply and quickly. It also allows the user to retain control of their BTC while it is deposited in a channel.
Finally, when they want to close their connection to the channel a user can simply submit to withdraw and close, which settles their account and sends back any unspent or received BTC to their wallet.
As an example, a grocery store could set up a channel which shoppers could join before depositing BTC into the grocery store channel under their address. They can then spend the deposited amount in the grocery store. Users can top up their BTC without having to close and re-open the connection and can leave BTC in the channel ready for spending another time.
Eventually the idea for Lightning is that everyone will be interconnected with one another through different channels, creating a mesh network so that sending and receiving from any wallet will become a seamless experience.
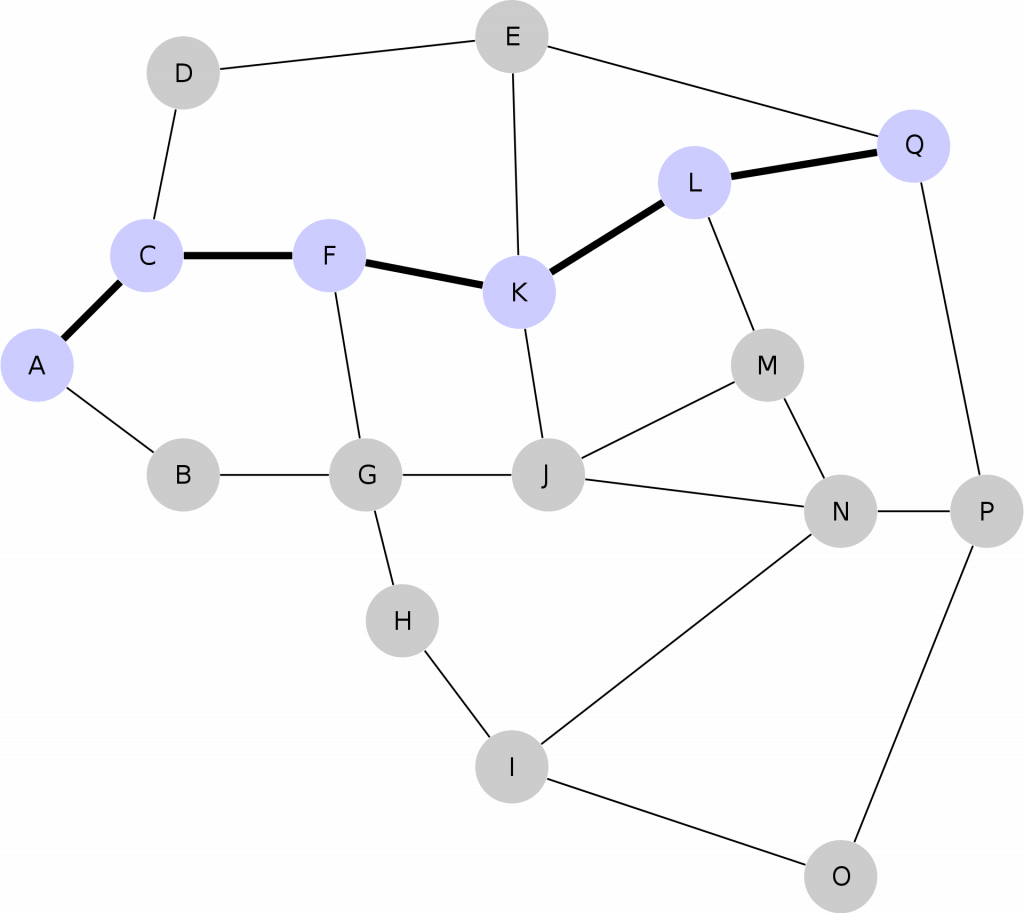
The image above shows routing through a mesh network. If User A wanted to send Bitcoin to user Q, the Bitcoin could be routed through other users, connected by different channels until it reaches the end recipient.
To use Bitcoin Lightning yourself, you’ll just need to download and fund a wallet such as Muun with BTC in order to send to other lightning wallets.
Benefits of the Bitcoin Lightning network
Lightning’s approach has a few extra benefits, one being that Bitcoin Lightning has the ability for smart contracts to be used on their network. While the usage of lightning smart contracts isn’t widespread, as Lightning is still in a beta stage, it provides a host of opportunities for the future of Bitcoin backed smart contracts. It also offers a way for the Bitcoin network to compete with newer blockchains which natively allow smart contracts such as Ethereum.
Another benefit is that it provides a further level of privacy. It’s much harder to track where a user spends their BTC as the spendings happen off-chain and are hidden within Lightning channels. All a user on the mainnet would see is the Bitcoin going into a multi-sig wallet with less being sent back out.
Drawbacks of the Bitcoin Lightning network
However, that increased privacy means losing control of the private keys that the BTC is stored on. When you deposit BTC into a channel, it means that multiple users need to agree to release a user’s funds – they must both confirm that the user has X amount of BTC that was deposited into the channel. Issues can occur when there is a dispute over how much one of them has, resulting in delayed withdrawals or, in the worst case scenario, loss of the BTC.
The BTC is also stored in hot wallets while it’s deposited in a channel, meaning deposits and withdrawals occur from them regularly and the private keys are stored on an internet connected machine. While it has yet to occur, it’s possible for a hacker to obtain the keys required to loot channels as it isn’t as secure as cold storage of Bitcoin.
Other vulnerabilities have also been identified, so as with anything in crypto it’s worth doing your own research so that you can fully understand the risks and benefits of using Bitcoin Lightning.
Applications of the Bitcoin Lightning Network
The most prominent real world use of Bitcoin lightning is in El Salvador where they ratified BTC as legal tender, meaning it can be used as an official payment method in the country. Bitcoin Lightning means that citizens can transact with Bitcoin as an everyday currency, helping decrease the cost of sending money across borders which can cost up to $195 in remittance fees.
Another upcoming application is Twitter, where the co-founder Jack Dorsey wanted to implement Bitcoin lightning to be used as a payment method. It’s speculated that Elon Musk may follow this idea through.
Alternatives to the Bitcoin Lightning Network
While Bitcoin lightning is probably the most popular Bitcoin L2, it isn’t the only one trying to improve Bitcoin beyond just simple transactions. Other L2’s such as Stacks and RSK mainly focus on providing smart contract support to Bitcoin, something which chains like Ethereum have dominated BTC on up to now.

Final thoughts
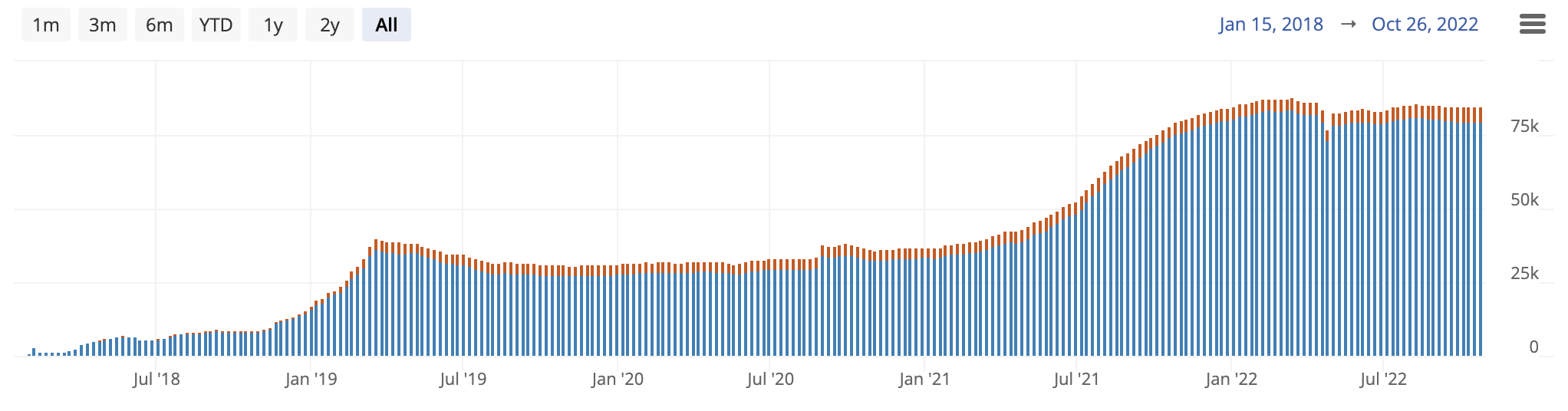
Currently Bitcoin lightning has $100m locked into the network with around 80,000 channels open – up from just 30,000 a year ago. Due to a rapid rise in crypto use around the world, Bitcoin Lightning has boomed in nearly every continent.
As use of crypto continues to grow, the innovation provided by the likes of Bitcoin lightning are becoming vital in keeping Bitcoin usable and competitive with newer chains. Who knows what new technology could arise next for Bitcoin, or where Bitcoin Lightning could be implemented next.
This piece of work does not contain investment advice. None of the information above should be considered as either advice or recommendation. Readers looking to invest should carry out their own research and make sure they are aware of the risks associated with trading.
