Published 1st September 2022
Ethereum 2.0: A Complete Guide

The transition or merge to Ethereum 2.0 has been the talk of the blockchain space for quite some time now. After years of delays, it appears that ETH 2.0 is finally about to come to fruition. We've put together everything you need to know about ETH 2.0's upcoming merge to the Mainnet.
Founder Vitalik Buterin launched Ethereum alongside co-founder Gavin Wood as an open-source blockchain that allows cryptocurrencies, NFTs and decentralised applications to be built on top of the network. As such, the Ethereum blockchain has become home to some of the most successful projects in the blockchain space, including Uniswap, Bored Ape Yacht Club and Decentraland.
Whilst Ethereum has become adopted by the masses, it doesn’t come without its issues. Low speeds and high costs have created a demand for a bigger, faster and ultimately better version of the network: Ethereum 2.0.
Why do we need ETH 2.0?
Scalability
Currently, Ethereum can only handle around 13 transactions per second (tps). Whilst this was at one time impressive due to being twice the amount Bitcoin can process, competing layer one blockchains have far surpassed this number.
By comparison, Polkadot can process around 1,000 tps, Solana can handle around 65,000 tps and Near Protocol is said to be able to support a staggering 100,000 transactions per second.
Due to Ethereum’s success, there are far more than 13 transactions needing to be processed every second. As all these transactions compete with one another, it causes the transaction (gas) fees to rise.
Consequently, Ethereum’s gas fees have risen to a level that has arguably made other blockchains more attractive, certainly cheaper. Avalanche, Polkadot, Solana as well as many more networks have become known as the Ethereum killers due to their ability to offer users far cheaper gas fees.
The introduction of sharding, which we’ll come on to later, means Ethereum 2.0 will support 100,000 tps making the Ethereum network far more scalable.

Sustainability
Ethereum operates using the proof-of-work (PoW) consensus. Miners use physical hardware to complete ‘blocks’ of verified transactions and in doing so act as a security mechanism on the blockchain.
However, this process comes at a cost. It’s incredibly energy intensive. You’ve likely read in the news how Bitcoin, which also uses proof-of-work, consumes the same amount of energy as a small country – which Elon Musk cited as a reason to stop accepting BTC as a form of payment for Tesla cars.
ETH 2.0 will employ a new proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus (which we’ll mention a lot in this guide) to be more eco-friendly.
Security and cost
Under the original proof-of-work (PoW) consensus model, the security that Ethereum provides is very costly. In order to incentivise miners, payouts are required as a reward for their work. These rewards come in the form of block rewards.
The concept is very simple, if you mine the block submitted to the Mainnet then you get the reward. However in order for it to be worth it, the payout has to be greater than the electricity cost that miners are putting into their hardware. If the payouts don’t exceed the energy costs, miners will start to turn off their hardware and the blockchain will be more susceptible to attack as gaining a 51% hashrate majority is easier.
Speaking at Devcon5 back in 2019, Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin outlined how Ethereum 2.0 will maximise the cost of attack for those who want to use the blockchain for illicit purposes.
Features of ETH 2.0
Proof-of-stake consensus
As you’ve probably gathered by now, the biggest difference between Ethereum 1.0 and 2.0 will be the switch from a proof-of-work (PoW) to a proof-of-stake (PoS) model.
Proof-of-work involves miners competing against each other to solve cryptographic puzzles and subsequently earn rewards for doing so. In the case of Ethereum, miners work to solve the cryptographic puzzles which verifies transactions on the Ethereum blockchain to earn ETH as a reward.
This consensus is extremely energy consuming due to miners building ‘farm-like’ systems of mining power which uses up enormous amounts of energy.
On the other hand, the proof-of-stake mechanism involves the selection of one node (or validator) to solve the puzzle which facilitates the minting of new blocks on the blockchain.
The vast majority of blockchains use proof-of-stake to benefit from transactions which are faster and cheaper for users.
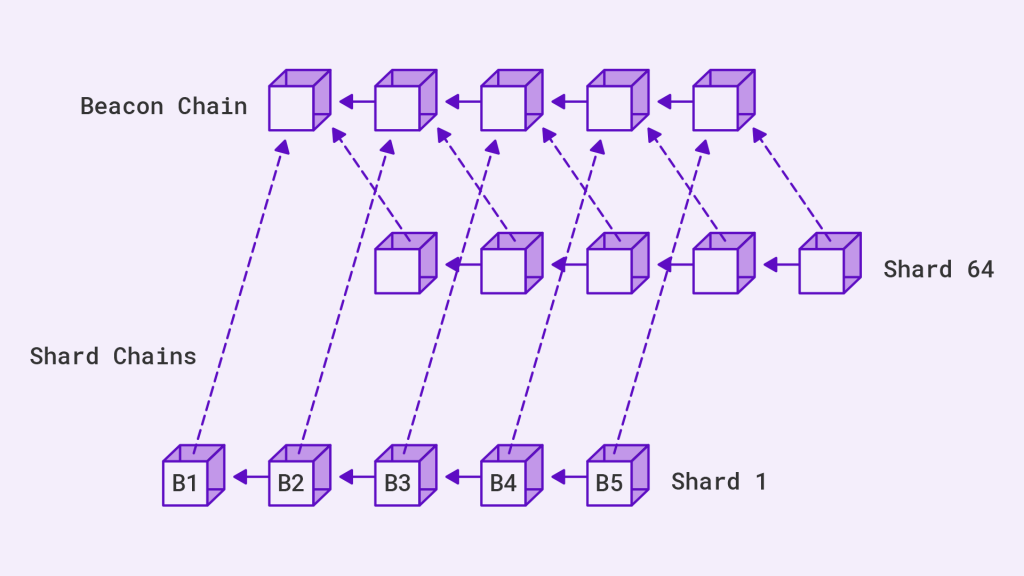
Beacon Chain
The thing that makes proof-of-stake possible is the Beacon Chain, which actually went live on the 1st December 2020 and has run parallel to the Ethereum Mainnet ever since. Once the merge is complete, Ethereum will shift from the Mainnet’s proof-of-work consensus to the Beacon Chain’s proof-of-stake consensus.
The Beacon Chain will be the heartbeat of Ethereum 2.0. You can think of the Beacon Chain as the body that oversees the transactions on the network the same way a lighthouse oversees ships at sea. Its role will include selecting and rewarding validators and also enforcing punishments for those with malicious intentions.
![]()
Sharding
As we mentioned earlier, Ethereum’s transactions per second are going to jump from 13 to 100,000. This is because of the introduction of sharding.
Currently, the Ethereum network has one chain which creates a traffic-jam-like effect when the network is busy. Sharding is the process of lowering the workload of nodes on the Ethereum network.
ETH 2.0 will contain 64 shards which you can think of as chains, responsible for processing transactions and data.
One of the 64 shards will be the current Ethereum blockchain. As such, we will be able to keep all current Ethereum data whilst also benefitting from 63 new blockchains.
It should be noted that the Ethereum website tells us sharding will be rolled out in multiple stages with the estimated completion date to be between 2023 and 2024.
Will ETH 2.0 reduce gas fees?
Whilst there’s no definitive answer on this, it’s certainly expected that ETH 2.0 will be the solution to Ethereum’s high transaction (gas) fees.
The ability to handle more transactions per second should in theory keep gas fees at a stable, reasonable level.
One Reddit user has worked out the math behind the merge and expects Ethereum gas fees to eventually drop lower than a cent.
When will ETH 2.0 launch?
Ethereum 2.0 was originally due to launch back in 2019 but has been delayed due to a variety of reasons. Most notably, Ethereum developers announced recently they were having issues with a piece of code named the difficulty bomb.
However, the arrival of ETH 2.0 is finally in sight. On 24th August, in a blog post on the Ethereum website, it was announced that the merge will be activated on the Beacon Chain on September 6th.
The transition is expected to be fully completed between September 10th-20th, 2022.
It will be exciting to see how this merge affects the blockchain space. Let us know your thoughts on Ethereum 2.0 via our socials.
This piece of work does not contain investment advice. None of the information above should be considered as advice or recommendation. Readers looking to invest should carry out their own research and make sure they are aware of the risks associated with trading.