Published 11th July 2021
Is Bitcoin a Scam?

If you’re wondering if Bitcoin is really all it’s made out to be, you’re not alone. With increased attention on the cryptocurrency thanks to the recent announcement of a Bitcoin ETF, many people are wondering if Bitcoin is a legitimate asset. But what really is Bitcoin?
What is Bitcoin and how does it work?
Bitcoin is the world’s first and most popular cryptocurrency. It was created in 2009 by pseudonymous coder Satoshi Nakamoto.
It is thought that Satoshi created Bitcoin in direct response to the public distrust of the current financial system following the 2008 financial crisis. The banks and systems entrusted with protecting the financial interests of the public failed, leading to a devastating global recession.
Traditional currencies, such as the US Dollar and British Pound, are typically inflationary. This means the government or central bank controlling the currency can inflate the supply based on their needs. In 2020 alone, the US created 22% of all USD in circulation since the birth of the nation, thanks to the COVID-19 crisis.
This alarming statistic has led many to worry about hyperinflation and the devaluation of American citizen’s hard-earned money. Similarly in the UK, British inflation has continually risen thanks to surging food costs, a shortage of workers and an expensive reliance on natural gas.
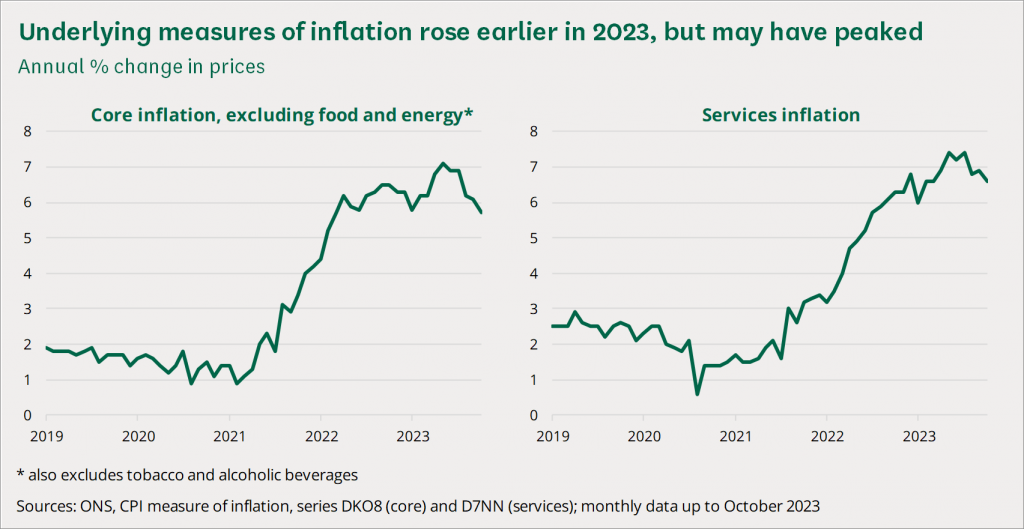
In contrast, the purpose of Bitcoin is to serve as a deflationary currency, meaning that its total supply is fixed, and its rate of supply decreases in regular intervals through what is known as ‘halvings’. This theoretically allows the currency to maintain its value over time, despite its volatility in the short and medium term.
The currency operates on a blockchain, which is a peer-to-peer network, functioning without the need for intermediaries like banks or lenders, as the network is validated by each member of the blockchain. It is also completely transparent, meaning every participant can see every transaction that occurs.
The primary role of a blockchain is to record information, achieved through a distributed ledger that replicates and disperses data across a network of participating computers. This design ensures there is no singular point of failure, rendering the network highly secure.
Is Bitcoin to be trusted?
While transactions on a blockchain are visible for all to see, the identities of those involved in the transactions are not. As such, there is a popular view that cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin only attract illicit activity.
Many leading figures, including the US Secretary of the Treasury Janet Yellen, have expressed their concern that Bitcoin was being heavily used by criminals and terrorist organisations. Despite this, financial institutions have begun investing in the cryptocurrency since its 2021 boom, such as JPMorgan, even though its CEO admitted that “personally I think Bitcoin is worthless”.

However, the US Secretary’s claims do not withstand scrutiny. Chanalysis, a blockchain data analysis firm, estimated that only 0.24% of total cryptocurrency transaction volume in 2022 consisted of illicit transactions.
It is perhaps understandable due to its mysterious nature and somewhat underground reputation that Bitcoin could be seen to help criminal activity, but the goal of money laundering, for example, is to create a chain of transactions that cannot be traced to one entity.
In reality, this makes Bitcoin quite a terrible solution for money laundering, thanks to the transparency of the public blockchain. Laundering money through Bitcoin leaves a permanent and unalterable trail of breadcrumbs. Even if a bad actor was to send the Bitcoin through multiple addresses, the funds will always be traceable with sufficient time and data-crunching capability.
As such, money laundering specifically was estimated by Chainalysis to make up only 0.05% of total transaction volume in 2021.
In fact, the usage of blockchain technology is actually overwhelmingly legitimate. Several large companies and institutions have now begun to use blockchain technology in their daily operations – such as Microsoft, Coca Cola, Mercedes-Benz and even Starbucks, just to name a few.

So to answer the question, no, Bitcoin is not a scam. It is a legitimate digital currency utilising an extremely useful and versatile new technology.
Can you lose real money on Bitcoin?
As with any financial asset, it is always possible to lose real money when investing. Bitcoin is no different. Cryptocurrency is known for its high volatility, and as such it is more likely for your investment to lose its value more rapidly than other assets, such as gold or stocks, where prices are generally more stable.
However, when looking at longer time scales, Bitcoin has proven itself as a good hedge against inflation. The cryptocurrency market has outperformed most financial markets, and the percentage gains of some cryptocurrencies can be astronomically high. Bitcoin was worth just $1,000 in 2017, and shot up to $68,000 in 2021. Of course, timing is everything, as Bitcoin is currently worth around $40,000 as of January 2024.
Before making any investment, it is important to do your own research (DYOR), and consider your own reasons for investing. Whether it’s a crypto or a stock, you should thoroughly research the project and the team behind it.
How many Bitcoin are there?
Bitcoin has a hard-coded max supply of 21 million Bitcoin. Once these have been mined, there will never be any additional Bitcoin created.
To mine a Bitcoin, certain users called ‘miners’ take the latest group of transactions and race to solve a complex mathematical puzzle called the ‘proof of work consensus algorithm.’ The purpose of the puzzle is to assign a hash to the group. The winning miner is rewarded with newly created Bitcoin. As of January 2024, the current reward is 6.25 Bitcoins.
However, as previously discussed, once a certain number of blocks are mined, this reward will be halved to 3.125 Bitcoins. The idea behind this is to sustain the emission and scarcity of Bitcoin, and this will continue until all 21 million Bitcoins have been mined. To understand this, we can compare it to gold.
Gold is very rare, and therefore quite difficult to find. This means that the more gold you find, the less there is for someone else to find. As more gold is mined, the amount of gold available increases, but the rate of supply decreases, as miners must search increasingly harder to find gold to mine. This is why gold has maintained its value for thousands of years.
Currently, around 93% of all Bitcoins have already been mined, but thanks to the halving cycles, the last remaining Bitcoin isn’t expected to be mined until 2140!
Is it smart to invest in Bitcoin?
With any investment, it is important to consider your own financial position, and decide what type of investment meets your personal needs. That being said, as a digital decentralised currency, Bitcoin has several advantages over traditional cash:
Fast transactions and low fees
Bitcoin isn’t subject to bank charges and government regulations. This means all transactions – including international ones – are fast and have minimal fees. Crucially, Bitcoin offers a solution for people in poorer countries without access to reliable banking.
For example, El Salvador was the first country to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender, allowing its citizens to utilise Bitcoin for daily living, as well as incentivising people to partake by providing a $30 sign-up bonus to the roll-out of their own digital wallet “Chivo”.
India, Nigeria and Vietnam are also the biggest early adopters of Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies generally, according to the 2023 Global Crypto Adoption Index.
Traditionally, international transfers can generally take 1-5 days, and must be approved by a number of intermediary authorities. Bitcoin transactions typically take around 10 minutes on average to be settled.
No inflation

As discussed, central banks create or reduce the supply of cash at will, whereas Bitcoin’s supply is completely fixed. This means that if more people buy Bitcoin, its value is guaranteed to increase.
A secure system that protects anonymity for its users
Although blockchain is a public ledger where you can see all the transactions, it doesn’t record users’ identities, so your personal details can’t be shared with a third party. Transactions are very secure because the blockchain is virtually impossible to hack.
To figure out why everyone is talking about Bitcoin, let’s take a closer look at how it works:
How does Bitcoin actually work?
To use Bitcoin, you must first create a wallet. We’ll talk more about types of wallets later, but all wallets provide the user with a means of crypto storage, using public and private keys, and the ability to interact with a blockchain. Your public key is a string of numbers available to the network (like a bank account number). Your private key is a secret string of numbers that confirms you’ve authorised a transaction (like a PIN).
When someone sends you Bitcoin, the network checks that the sender’s public key has enough funds to make the payment and that the private key was used to authorise it.
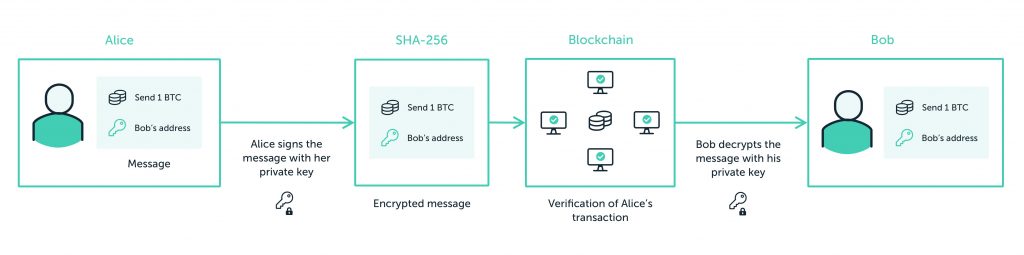
Next, miners solve the latest batch of transactions, and the miner who solves the puzzle broadcasts the batch to the network together with its hash, and the group is added as the latest block in the chain. This block of transactions – including your payment – is now immutable and your public key balance has been updated.
The proof of work algorithm is another layer of security; because puzzles take so much energy to solve, it’s counterproductive for hackers to tamper with the mining process.
How do I buy Bitcoin?
The easiest way to buy Bitcoin is via a cryptocurrency exchange. These exchanges allow you to purchase Bitcoin with traditional currency. Here are some popular ones:
Coinbase

Founded in 2011, Coinbase is the largest US Dollar exchange out there. Coinbase specialises in a simple and easy-to-use interface, making it highly recommended for those new to crypto. However, they benefit from user naivety by having markedly high transaction fees compared to other exchanges.
Binance

The world’s largest crypto exchange, offering very low transaction fees and a wide range of resources to teach users about blockchain and Bitcoin in their Binance Academy. They offer a huge range of cryptocurrencies compared to Coinbase, which in turn means a greater amount of risk if investing in lesser known coins. Remember, do your own research (DYOR).
Kraken

Kraken is the third-largest exchange by trading volume, and offers a number of services similar to Binance. Kraken offers even lower fees than Binance, making it especially useful for high-volume traders, but offers a smaller range of coins.
Like anything in the digital world, it is good practice to have excellent privacy and security measures in place. We suggest when you start your journey into the world of crypto to create a separate email address. This will mean that if your email address is compromised then your information regarding your crypto activities will still be safe.
Can you cash out Bitcoin for real money?
The easiest way to cash out your Bitcoin is again through a cryptocurrency exchange like Coinbase or Binance. Coinbase specifically offers a number of currencies such as the US Dollar, British Pound and the Euro.
In some countries, there are even Bitcoin ATMs where you can sell your Bitcoin on the street.
Where is the best place to hold crypto?
You can store your Bitcoin on the exchange you bought it from, or on a digital wallet. It is highly recommended to use a hardware wallet if you mean to hold your crypto long-term.
Keeping your Bitcoin on the exchange is convenient, but the downside is you don’t control the keys for your coin – they’re controlled by the exchange. If the exchange has a lapse in security, or indeed completely collapses, your coin could be vulnerable to theft or loss.
Most people opt for a digital wallet – software that contains your public and private keys and interacts with the blockchain, keeping a record of your balance. A wallet lets you have full control over your keys.
Wallets can be online (hot wallets) or offline (cold wallets). Each version has unique benefits:
Hot wallets
Hot wallets are a good choice if you want to make regular transactions with your Bitcoin. They’re typically free, easy to set up and access.
However, a hot wallet could potentially be a target for hacks because your keys are connected to the internet. For this reason, it’s best not to store high amounts of Bitcoin on it. Some popular hot wallet choices include MetaMask and Trust.
Cold wallets
Cold wallets are the safest way to store your Bitcoin because your keys are kept offline. They’re a good choice if you have a lot of Bitcoin and you don’t need to access it too often.
Cold wallets are typically physical wallets that work like a USB drive. They aren’t free; prices can vary from £40 to £170. Popular cold wallets include Ledger and Trezor.

Of course, this means that the wallet is susceptible to your own organisation. If you lose your wallet, or it’s stolen, your Bitcoin is gone forever.
Wallets can only do so much in terms of security, so whichever type of wallet you use, it’s essential to keep your private key safe and secret. Your private key is needed to access your wallet. Lose it, and you lose your Bitcoin.
Can I get my money back if I got scammed from Bitcoin?
The unfortunate consequence of cutting out intermediaries means that your transaction is rarely insured. Therefore, Bitcoin transactions are typically not reversible.
Will the Bitcoin ETF increase the price of Bitcoin?
You may have heard the recent rumours about the proposed Bitcoin Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs). Although not currently approved, the news has caused a surge of interest in the cryptocurrency. To understand what this means for Bitcoin, we first need to understand what an ETF actually is:
What is an ETF?
An ETF is an exchange-traded fund, which as its name suggests means it can be traded on an exchange, just like crypto coins or stocks. The price of an ETF’s shares will therefore change throughout the day as the shares are bought and sold. An ETF can be for any underlying asset or index, such as gold stocks or the S&P 500.
A Bitcoin ETF will work the same way, with the price of one share of the ETF fluctuating due to the price of Bitcoin. The only difference would be that the ETF could be traded on a market exchange like the NYSE or the NASDAQ. A Bitcoin ETF effectively brings Bitcoin to Wall Street.

Is it a good idea to invest in a Bitcoin ETF?
The release of Bitcoin ETFs will open up the Bitcoin market to a far more mainstream audience of investors, making Bitcoin investment more convenient, and attracting a new wave of institutional investors to the market. There will be no need to sign up to a crypto exchange, and existing investors will be able to invest in Bitcoin through their existing investment accounts.
Additionally, as an ETF can hold more than just one asset, Bitcoin ETFs could contain, for example, not only Bitcoin, but also Apple or Microsoft stocks. This would allow investors to easily diversify their holdings.
Given that Bitcoin is currently unregulated and completely decentralised, the majority of the world’s tax havens and pension funds do not allow for purchases of Bitcoin. A Bitcoin ETF would be traded on traditional exchanges, and therefore regulated by the SEC and other financial authorities, improving tax efficiency.
What is the disadvantage of a Bitcoin ETF?
The major drawback of a Bitcoin ETF is that an ETF is naturally centralised, as the fund is managed by a bank or financial institution. This naturally undermines the very concept of Bitcoin as a decentralised digital currency for users interacting with the ETF.
Bitcoin also protects users through anonymity on the network, a benefit that would also be eliminated by a Bitcoin ETF, as the ETF would be regulated by the government. Additionally, a Bitcoin ETF would no longer serve the user as a currency, and would not be exchangeable with other cryptocurrencies, undermining its intended use case.
Is buying a Bitcoin ETF the same as buying Bitcoin?
No, buying an ETF is not the same as buying a Bitcoin, or any asset. This is because you are buying into a managed fund, not the asset itself. If you want full control and actual ownership of your Bitcoin, it will always be best to buy it directly.
Final thoughts
We hope this guide has helped dispel the myth that Bitcoin is a scam, and given you the basics of how Bitcoin works – and the benefits it offers. Pay with Bitcoin for lower fees; invest in Bitcoin for a safe-haven asset like gold.
As Bitcoin becomes more mainstream it will revolutionise money, offering a fair and secure alternative to traditional currencies. But because Bitcoin is decentralised, the onus is on you to research reputable markets and protect your keys.
However, Bitcoin ETFs may provide users who don’t want the responsibility of holding keys to get in on the financial growth of Bitcoin, without the additional benefits of actual ownership.
Have you any thoughts on the future of Bitcoin? Contact our web3 design studio via X and check out our News page to learn more about Bitcoin and blockchain innovations.
This piece of work does not contain investment advice. None of the information above should be considered as either advice or recommendation. Readers looking to invest should carry out their own research and make sure they are aware of the risks associated with trading.